Carbon compounds =fats and oil 1
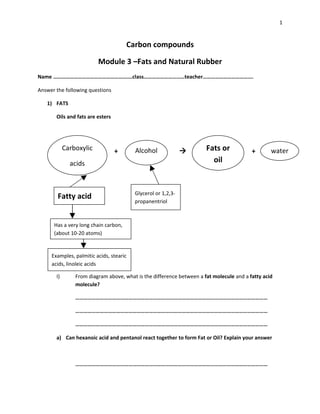
- 1. 1 Carbon compounds Module 3 –Fats and Natural Rubber Name ………………………………………………….class…………………………teacher………………………………. Answer the following questions 1) FATS Oils and fats are esters Carboxylic + Alcohol Fats or + water acids oil Glycerol or 1,2,3- Fatty acid propanentriol Has a very long chain carbon, (about 10-20 atoms) Examples, palmitic acids, stearic acids, linoleic acids I) From diagram above, what is the difference between a fat molecule and a fatty acid molecule? …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… a) Can hexanoic acid and pentanol react together to form Fat or Oil? Explain your answer ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
- 2. 2 b) Can decanoic acid and glycerol react together to form Fat or Oil? Explain your answer …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… c) State 2 similarities between fats and oils? …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… d) Fill in the table below to list differences between oils and fats. Oils Fats a) sources b) Physical state at room temperature c) Melting point d) Fill in the table below to list differences between saturated and unsaturated fats Unsaturated fats Saturated fats a) Proportion of molecules between saturated and unsaturated fats b) Physical state at room temperature c) Melting point d) sources e) Why do unsaturated fats turn bad or spoil easily?
- 3. 3 …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… f) Explain how unsaturated fats can be changed to saturated fats? ………………………………………………………………………………………………….. ………………………………………………………………………………………………….. ………………………………………………………………………………………………….. 2) Natural rubber a) List examples of natural polymers and their monomers polymers monomers 1 Starch 2 Cellulose 3 Protein 4 Rubber b) Draw the structural formula of natural rubber ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. c) State the properties of natural rubber
- 4. 4 i) White ………………………………… at room temperature ii) Elsticity that …………………………………………… overtime iii) Soft iv) Sensitive to ………………………………….. d) State 3 uses of natural rubber i) ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ii) ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. iii) ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. COAGULATION OF LATEX -PROCESS I) Latex is a ………………………………………………………… II) It consists of ………………………………………….particles dispersed in ………………………………… III) Each rubber particle is made-up many long-chain …………………………………………..molecules enclosed by a …………………………..-like membrane which is ……………………………charged Draw diagram of one rubber particle
- 5. 5 DESCRIBE THE COAGULATION OF LATEX i) The repulsion between the …………………………………………..charged particles prevent the ………………………………..particles from coming close to each other. Therefore latex could not ………………………………………… Draw diagram ii) When an ………………………………………is added to latex, OR when latex is exposed to ……………………………….., the …………………………..from the air enters the latex and produce ………………………………………..acid that form ……………………ions. This ……………………………….ions neutralize the …………………………………charges on the protein membrane. Draw diagram
- 6. 6 iii) The rubber ………………………………………..can now come close together. This enable them to ………………………………………….with one another resulting in the ………………….. of the protein membranes. Draw diagram iv) The rubber molecules …………………………………… with one another and get …………………………….. and thus causing latex to ……………………………. Draw diagram IV) Describe how to prevent the coagulation of latex
- 7. 7 By adding …………………………………….solution, that contains ……………………………….ions which ………………………………………. The acid produced by the bacteria . Therefore rubber particles remain …………………………………… charged and the coagulation is …………………. VULCANISED RUBBER a) What is meant by vulcanization of rubber? …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. b) In industry, how does the vulcanization of rubber is carried out? By heating latex with ……………………………………….. OR ……………………………………………. c) Describe how sulphur atoms change the properties of rubber In vulcanization , ………………….atoms form cross-………………between rubber ………………… These cross ……………………………………….prevent rubber …………………………..from sliding too much when ………………………………………….. The rubber molecules return to their ………………………………….. position after being stretched. d) Draw cross-linkage of sulphur
- 8. 8 e) Compare and contrast the properties of vulcanized and unvulcanised rubber Similarities Both are ……………………………………………………………… Both are ……………………………………………………………. Differences Vulcanised Differences Unvulcanised rubber Elasticity Hardness Tensile strength Resistance to heat Effect of organic solvents a) State one advantage of natural rubber over synthetic rubber Only natural rubber can take the tremendous ………………………, ……………………. and ………………………………produced during landing and taking off of an …………………….. TQ TQTQTQ
