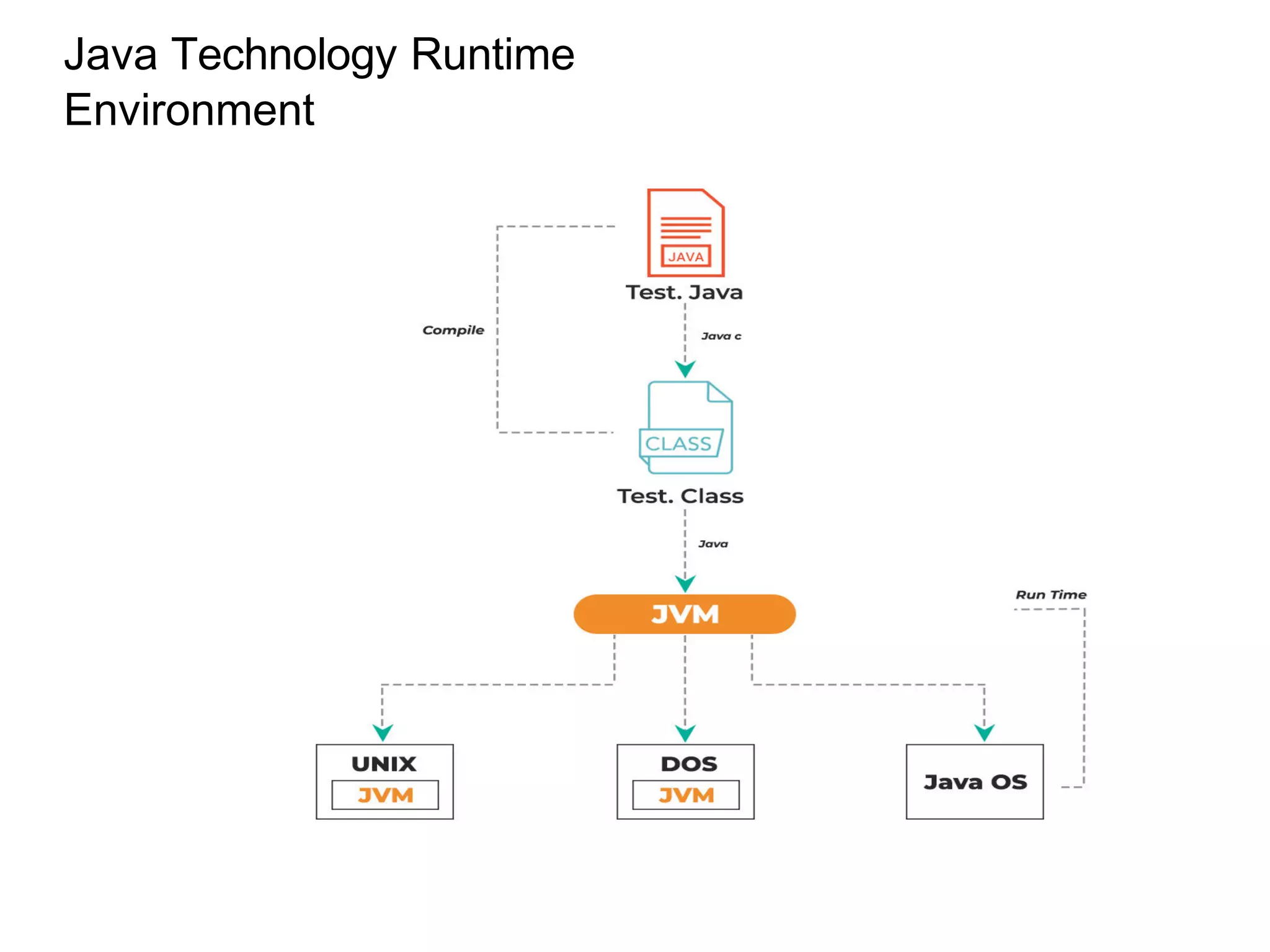
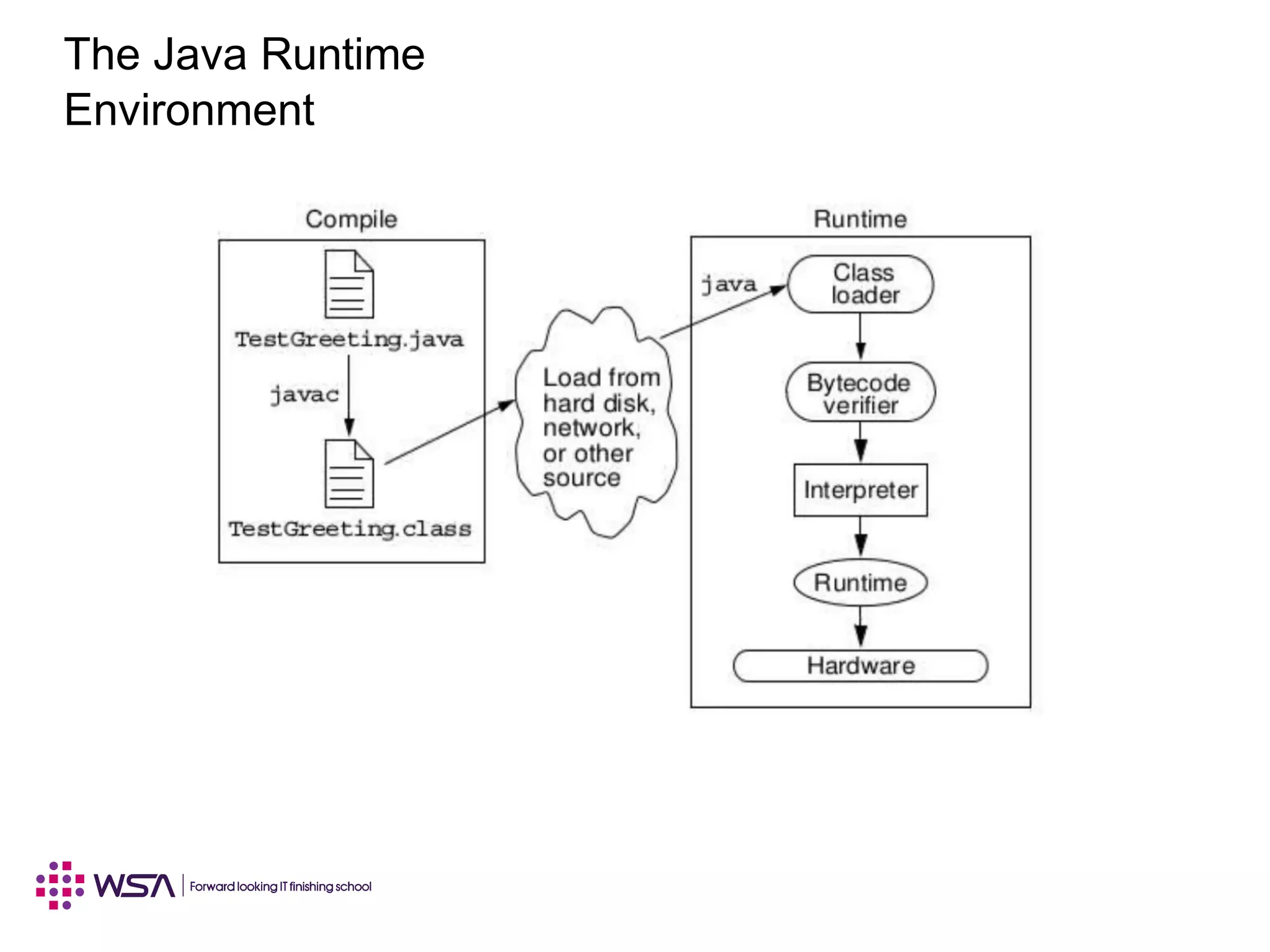
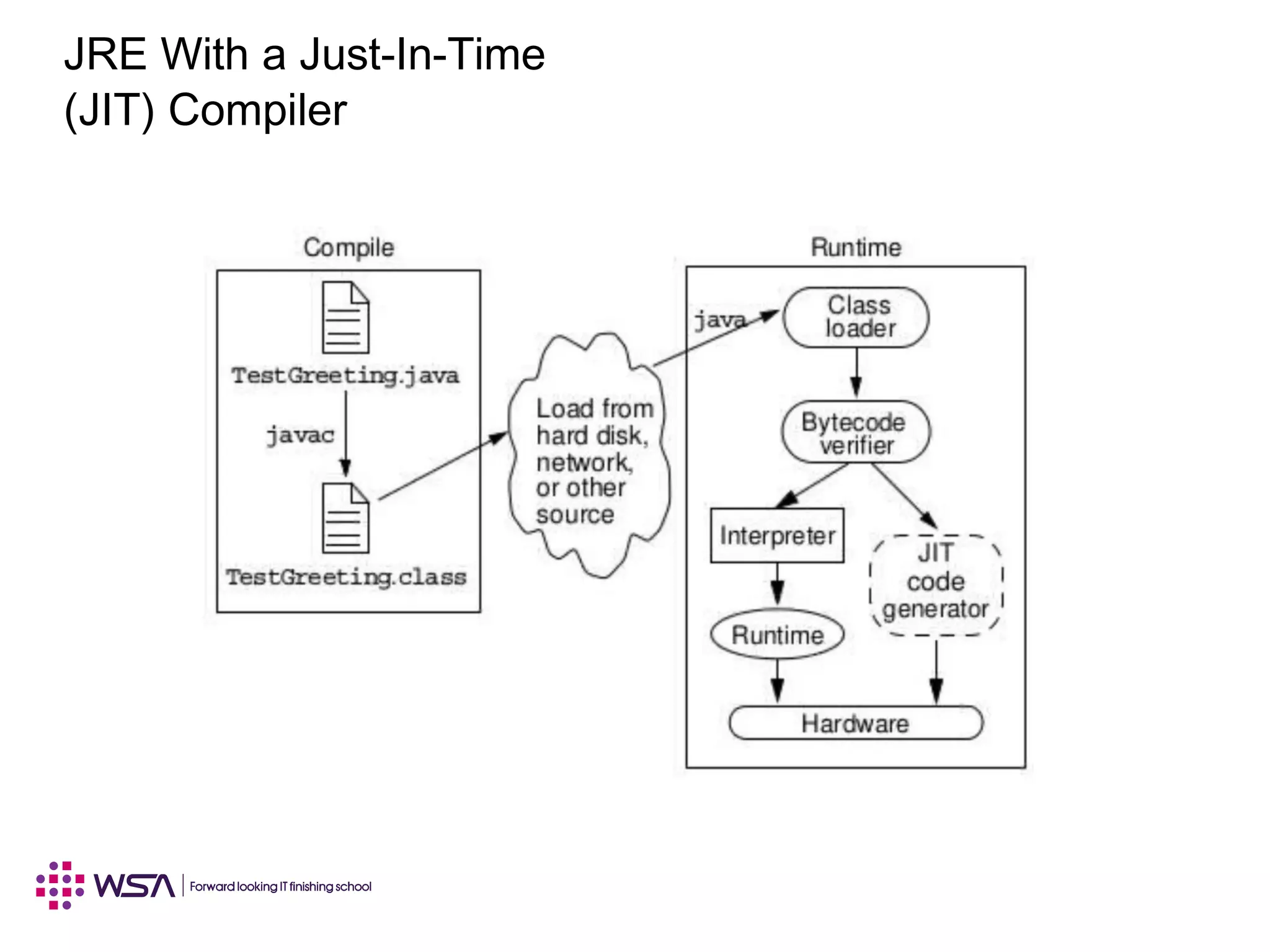
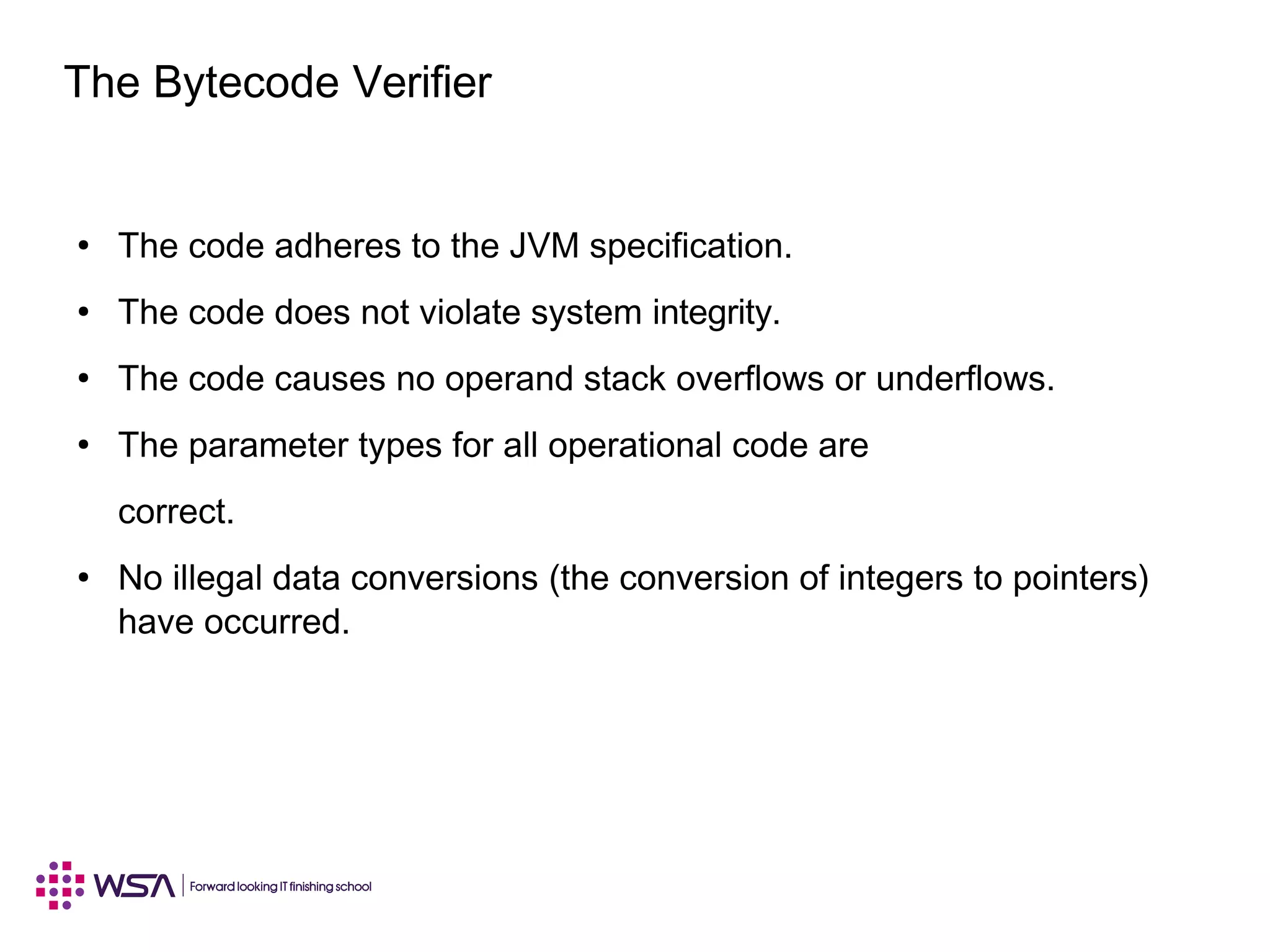
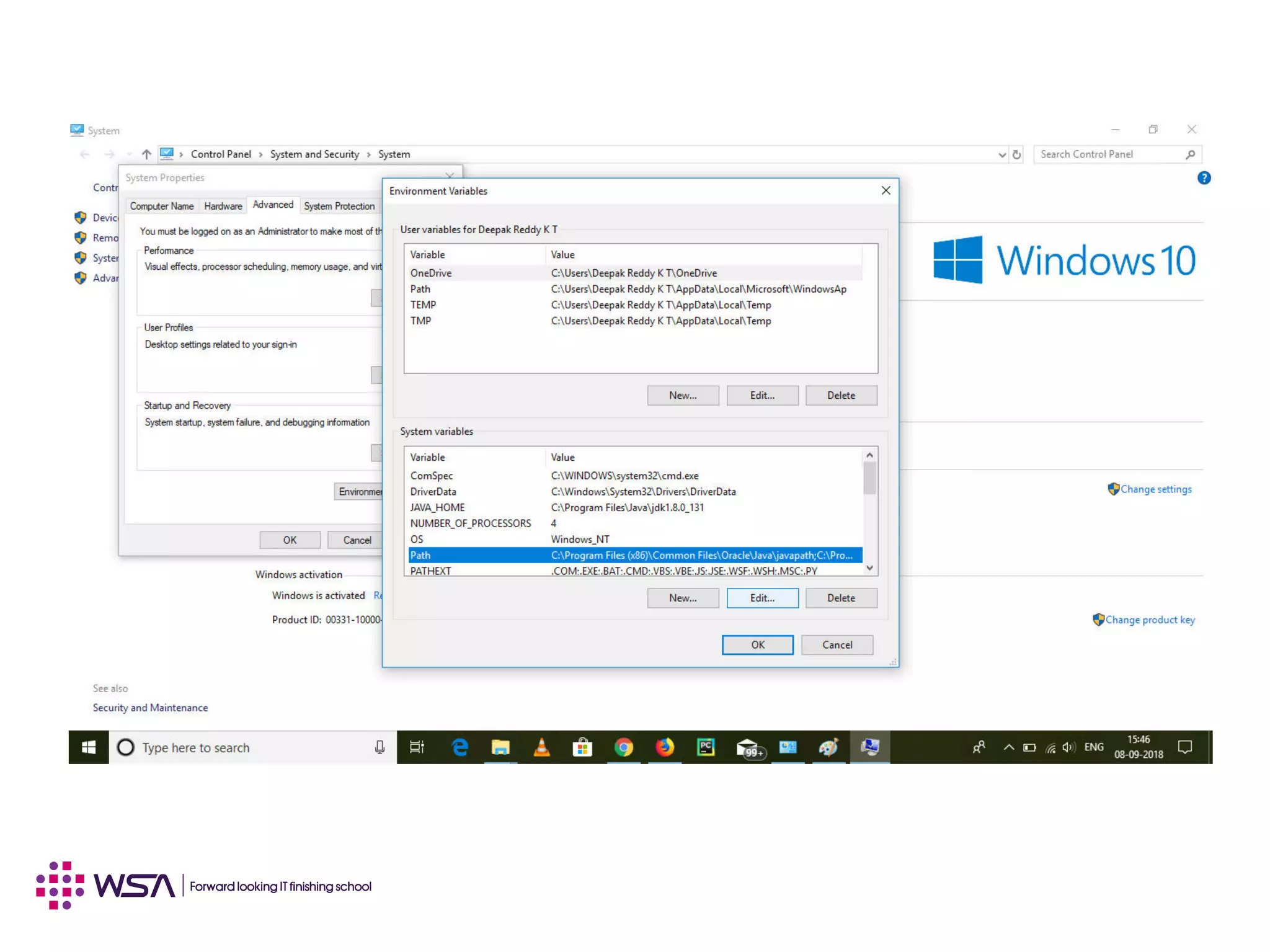
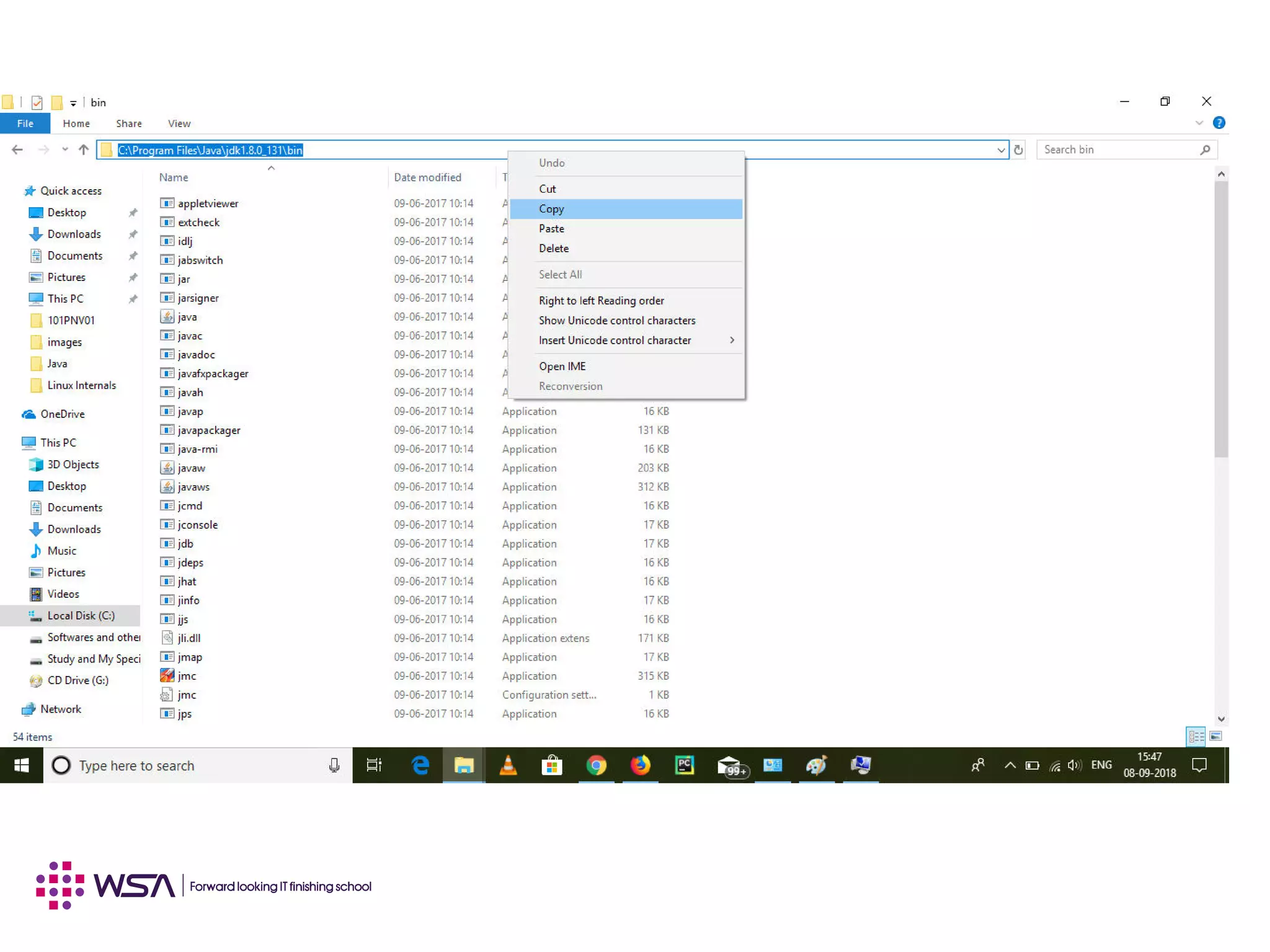
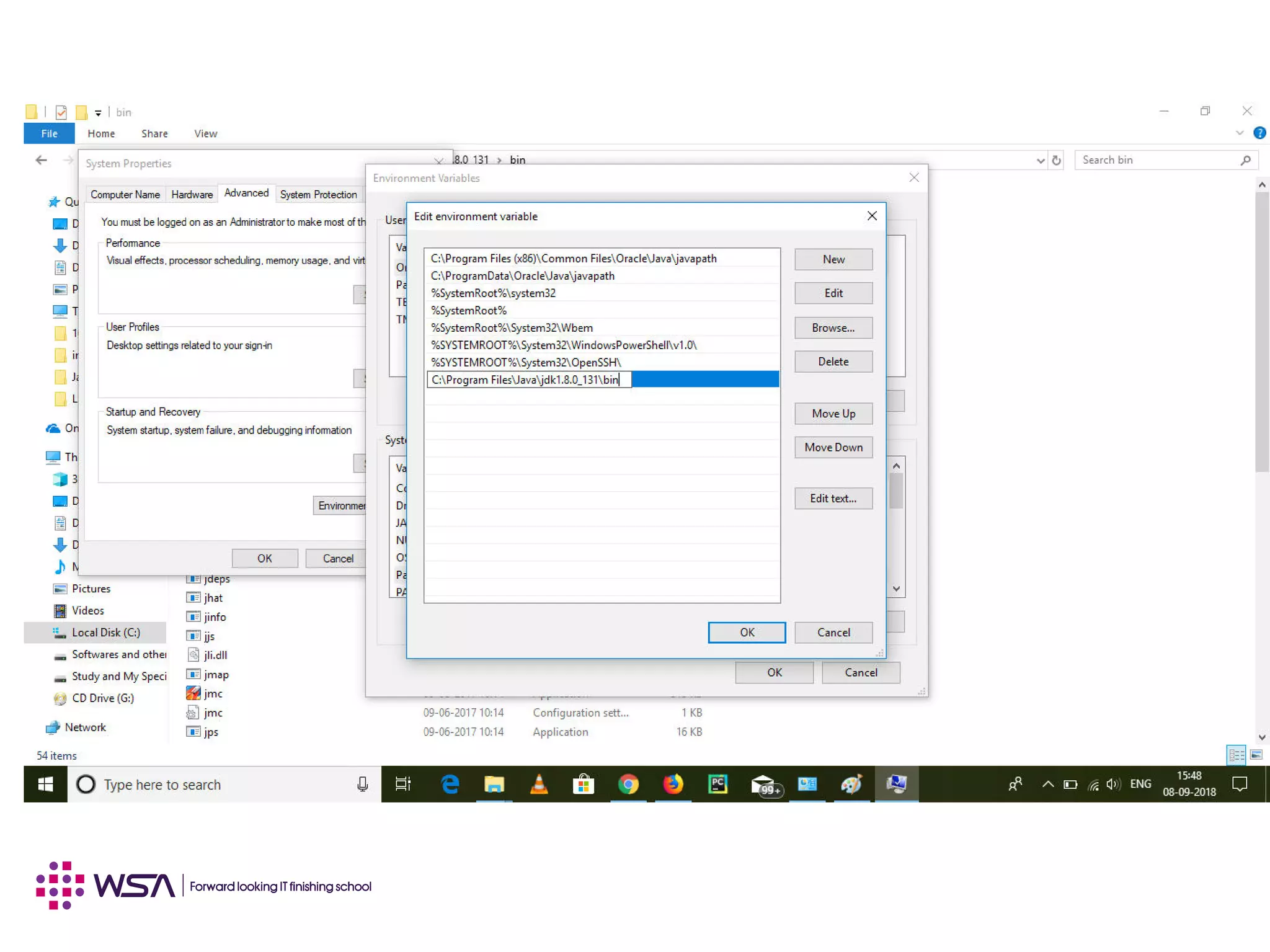
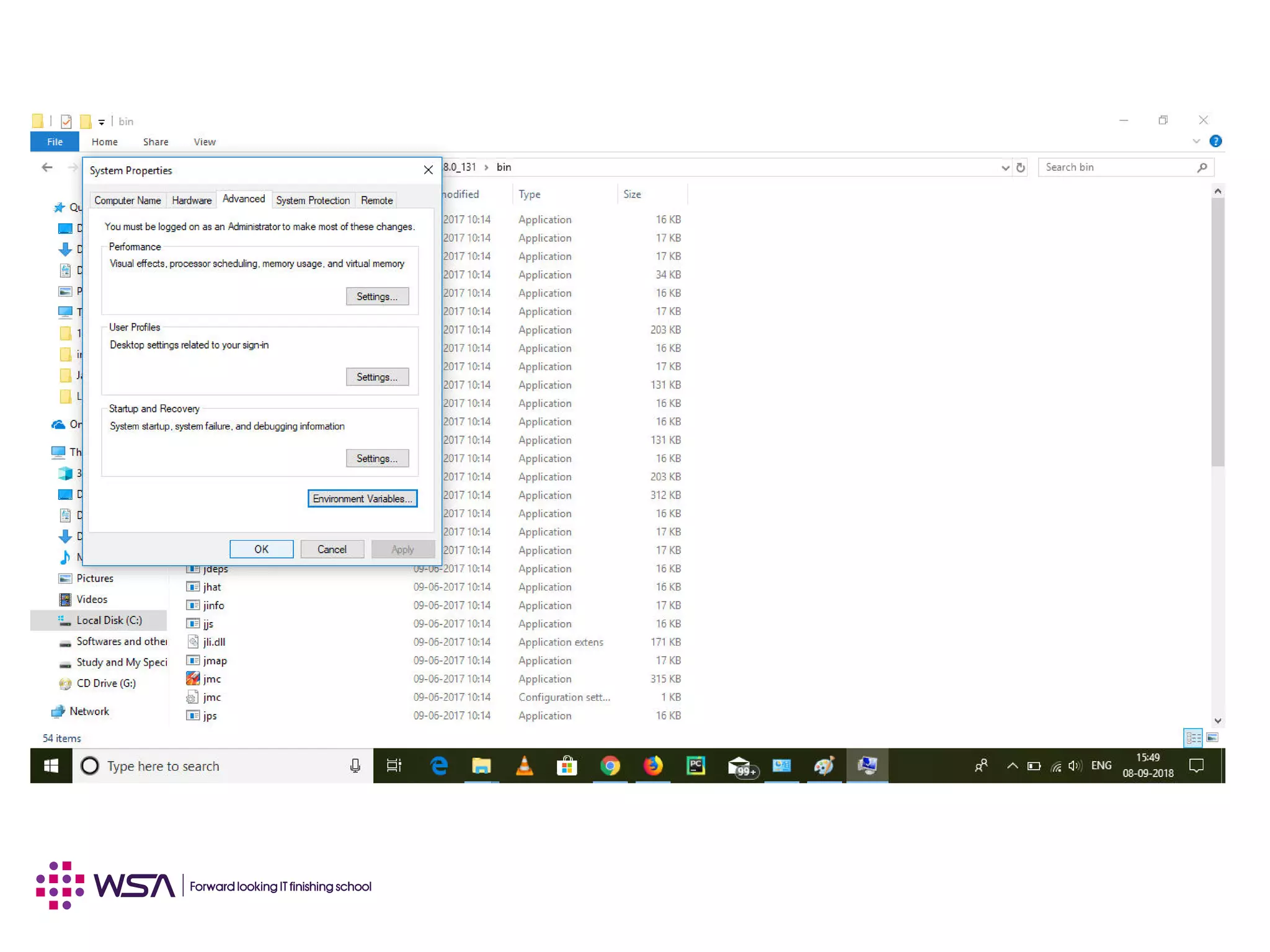
Java is a programming language and development environment used to build mobile and web applications. The key features include being object-oriented, avoiding common pitfalls of other languages, and providing code portability. The Java Virtual Machine (JVM) allows code to run on any platform and provides security features like dynamic class loading and garbage collection. A simple Java application can be written, compiled using javac, and run using java to output "Hello World".







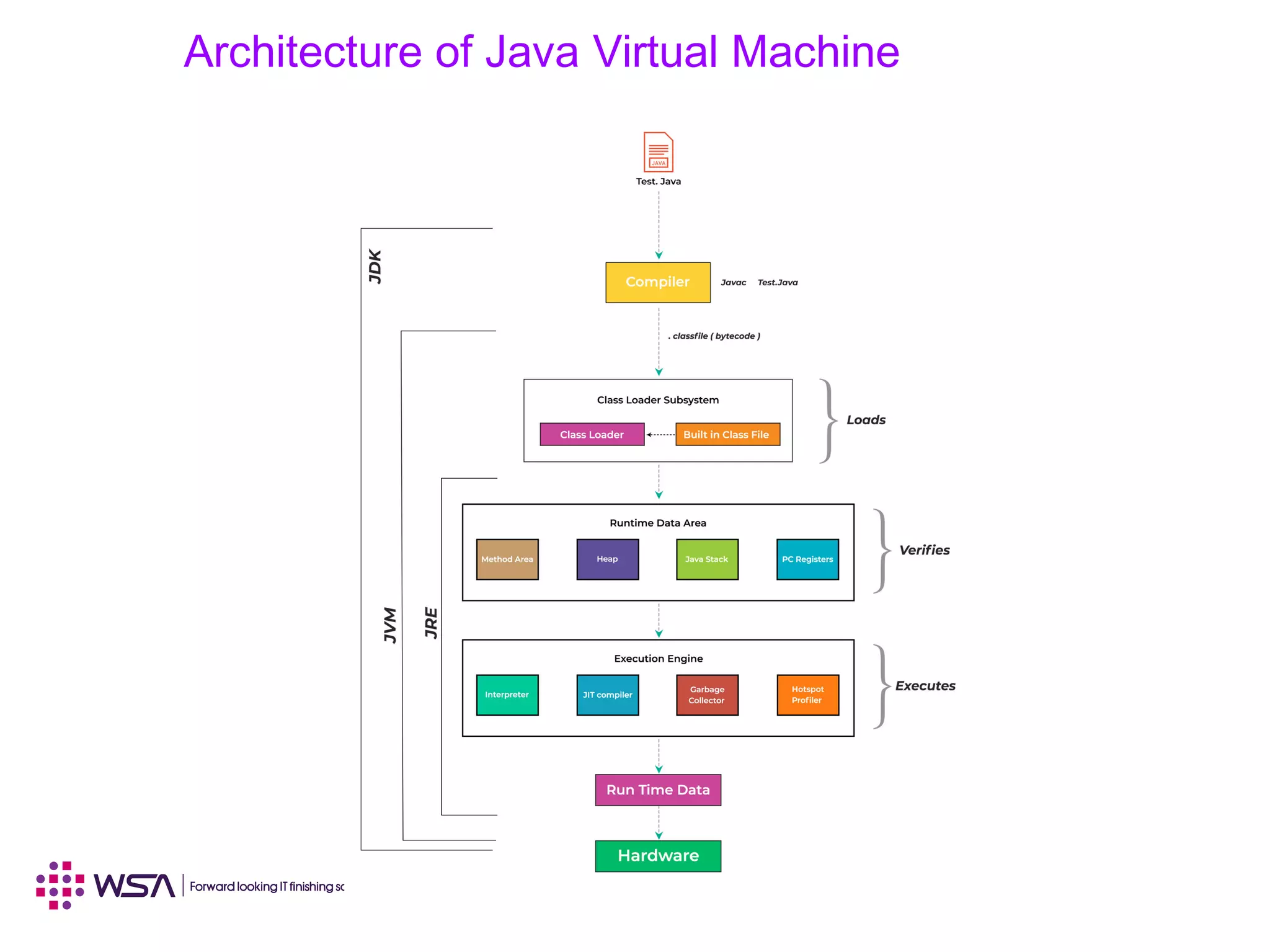
![The Java Virtual Machine
JVM provides definitions for the:
Instruction set (central processing unit [CPU])●
Register set●
Class file format●
Stack●
Garbage-collected heap●
Memory area●
Fatal error reporting●
High-precision timing support●](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/001javasegettingstarted-190429122455/75/Core-Java-Programming-Language-JSE-Chapter-I-Getting-Started-10-2048.jpg)





![A Simple Java Application
The Test.java Application
//
// Sample "Hello World" application
//
public class Test{
public static void main (String[] args) {
System.out.println(“Hello World”);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/001javasegettingstarted-190429122455/75/Core-Java-Programming-Language-JSE-Chapter-I-Getting-Started-37-2048.jpg)