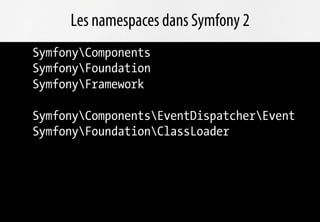
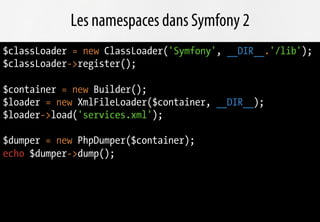
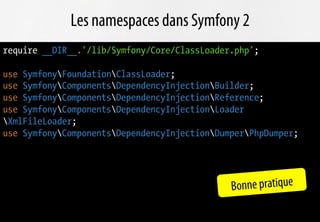
Le document présente les avantages de la migration vers PHP 5.3, notamment en termes de performance et d'interopérabilité grâce aux nouveaux standards de développement. Il souligne l'importance des frameworks modernes comme Symfony et Doctrine, qui tirent parti des nouvelles fonctionnalités de PHP 5.3 comme les namespaces et les fonctions anonymes. L'adoption rapide de PHP 5.3 dans les entreprises est anticipée, favorisant l'évolution des usages et la professionnalisation des développeurs.

























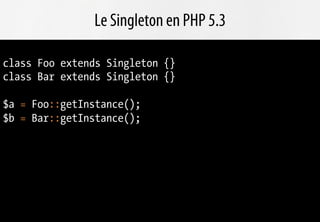
![Le Singleton en PHP 5.3
abstract class Singleton
{
private static $instances = array();
final private function __construct()
{
if (isset(self::$instances[get_called_class()]))
{
throw new Exception("An instance of ".get_called_class()." already exists.");
}
static::initialize();
}
protected function initialize() {}
final public static function getInstance()
{
$class = get_called_class();
if (!isset(self::$instances[$class]))
{
self::$instances[$class] = new static();
}
return self::$instances[$class];
}
final private function __clone() {}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/playing-with-php53-091113031526-phpapp01/85/Playing-With-PHP-5-3-32-320.jpg)




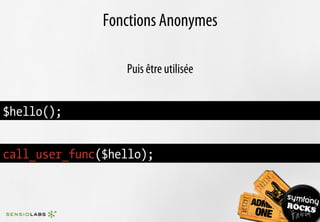



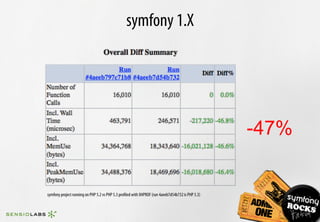
![$titles = array();
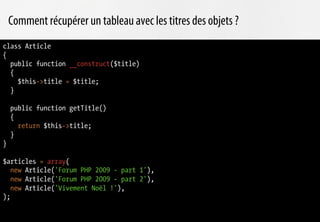
foreach ($articles as $article)
{
$titles[] = $article->getTitle();
}
100 100
$titles = array_map(create_function('$article', 'return $article->getTitle();'), $articles);
300 1800
$titles = array_map(function ($article) { return $article->getTitle(); }, $articles);
100 200
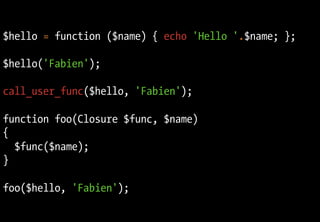
$mapper = function ($article) { return $article->getTitle(); };
$titles = array_map($mapper, $articles);
100 180
mémoire rapidité](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/playing-with-php53-091113031526-phpapp01/85/Playing-With-PHP-5-3-44-320.jpg)







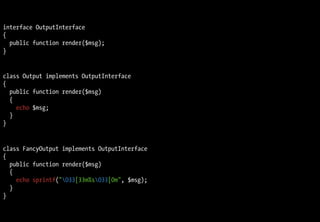
![class Message
{
public function __construct(OutputInterface $output, array $options)
{
$this->output = $output;
$this->options = array_merge(array('with_newline' => false), $options);
}
public function say($msg)
{
$this->output->render($msg.($this->options['with_newline'] ? "n" : ''));
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/playing-with-php53-091113031526-phpapp01/85/Playing-With-PHP-5-3-52-320.jpg)
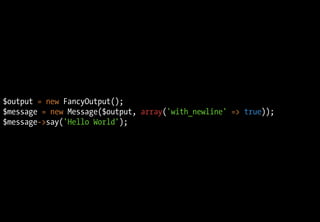

![class DIContainer
{
protected $values = array();
function __set($id, $value)
{
$this->values[$id] = $value;
}
function __get($id)
{
if (is_callable($this->values[$id]))
{
return $this->values[$id]($this);
}
else
{
return $this->values[$id];
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/playing-with-php53-091113031526-phpapp01/85/Playing-With-PHP-5-3-56-320.jpg)
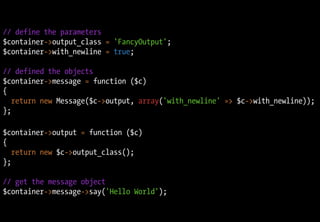

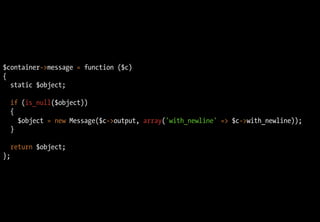

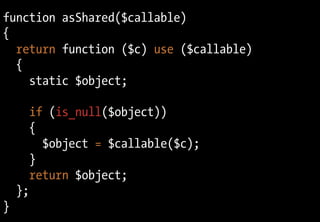
![class DIContainer
{
protected $values = array();
function __set($id, $value)
{
$this->values[$id] = $value;
}
function __get($id)
{
if (!isset($this->values[$id]))
{
throw new InvalidArgumentException(sprintf('Value "%s" is not defined.', $id));
}
if (is_callable($this->values[$id]))
{
return $this->values[$id]($this);
}
else
{
return $this->values[$id];
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/playing-with-php53-091113031526-phpapp01/85/Playing-With-PHP-5-3-63-320.jpg)
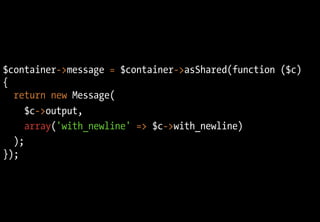
![class DIContainer
{
protected $values = array();
function __set($id, $value)
{
$this->values[$id] = $value;
}
function __get($id)
{
if (!isset($this->values[$id]))
{
throw new InvalidArgumentException(sprintf('Value "%s" is not defined.', $id));
}
if (is_callable($this->values[$id]))
{
return $this->values[$id]($this);
}
else
{
return $this->values[$id];
}
}
function asShared($callable)
{
return function ($c) use ($callable)
{
static $object; 40 LOC pour un
if (is_null($object))
{
$object = $callable($c);
co ntainer DI complet
}
return $object;
};
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/playing-with-php53-091113031526-phpapp01/85/Playing-With-PHP-5-3-64-320.jpg)

![Twittee: A Dependency Injection Container in a tweet
• Implementation does not use PHP 5.3
• Its usage needs PHP 5.3
class Container {
protected $s=array();
function __set($k, $c) { $this->s[$k]=$c; }
function __get($k) { return $this->s[$k]($this); }
}
witte e.org
t](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/playing-with-php53-091113031526-phpapp01/85/Playing-With-PHP-5-3-66-320.jpg)




![// an anonymous listener
$listener = function ($parameters)
{
echo "Hello {$parameters['name']}n";
};
// register the listener with the dispatcher
$dispatcher = new EventDispatcher(array(
'foo' => $listener,
));
// notify the event somewhere
$dispatcher->notify('foo', array('name' => 'Fabien'));](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/playing-with-php53-091113031526-phpapp01/85/Playing-With-PHP-5-3-71-320.jpg)
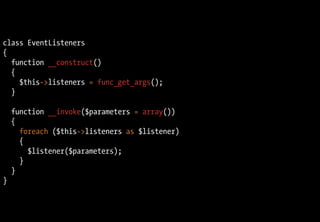
;
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/playing-with-php53-091113031526-phpapp01/85/Playing-With-PHP-5-3-72-320.jpg)
![Comment enregistrer plusieurs observateurs ?
$listener = new EventListeners(
function ($parameters) { echo "Hello {$parameters['name']}?n"; },
function ($parameters) { echo "Hello {$parameters['name']}!n"; }
);
$dispatcher = new EventDispatcher(array(
'foo' => $listener
));
$dispatcher->notify('foo', array('name' => 'Fabien'));](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/playing-with-php53-091113031526-phpapp01/85/Playing-With-PHP-5-3-73-320.jpg)