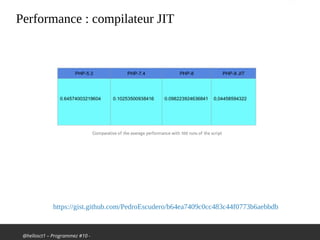
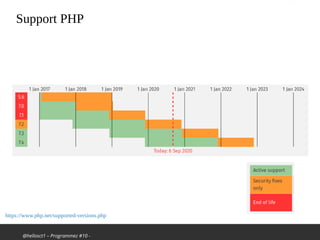
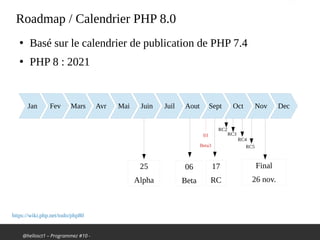
Le document traite des nouveautés et améliorations de PHP 8, comme le compilateur JIT, les types d'union, les attributs et les fonctions str_contains(), str_starts_with() et str_ends_with(). Il mentionne également les changements dans le traitement des erreurs et des avertissements, ainsi que des dépréciations de certaines fonctions. La présentation est faite dans le cadre d'un meetup sur PHP, célébrant les 25 ans de PHP et les 20 ans de l'AFUP.











![@hellosct1 – Programmez #10 -
Weath Maps (2/3)
●
Utilisation :
– Suppression des objets lorsque seul le cache fait référence
aux classes d’entités des objets.
– Economie des ressources lors de la manipulation des objets.
class FooBar {
private WeakMap $cache;
public function getSomethingWithCaching(object $obj)
{
return $this->cache[$obj] ??=
$this->computeSomethingExpensive($obj);
}
// ...
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/etes-vous-pret-pour-php8-200910065911/85/Etes-vous-pret-pour-php8-15-320.jpg)
![@hellosct1 – Programmez #10 -
WeathMaps (3/3)
●
Utilisation Tableau
$map = new WeakMap; // objet instancé
$obj = new stdClass;
$map[$obj] = 42;
var_dump($map);
Résultat :
object(WeakMap)#1 (1) {
[0]=>
array(2) {
["key"]=>
object(stdClass)#2 (0) { }
["value"]=> int(42)
}
}
unset($obj); // détruit variable
var_dump($map);
Résultat :
object(WeakMap)#1 (0) {}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/etes-vous-pret-pour-php8-200910065911/85/Etes-vous-pret-pour-php8-16-320.jpg)

![@hellosct1 – Programmez #10 -
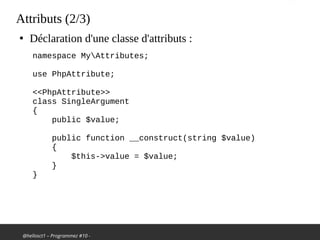
Attributs (3/3)
●
Exemple
<?php
use DoctrineORMAttributes as ORM;
use SymfonyComponentValidatorConstraints as Assert;
<<ORMEntity>>
class User
{
<<ORMId>><<ORMColumn("integer")>><<ORMGeneratedValue>>
private $id;
<<ORMColumn("string", ORMColumn::UNIQUE)>>
<<AssertEmail(array("message" => "The email '{{ value }}' is not a valid email."))>>
private $email;
<<AssertRange(["min" => 120, "max" => 180, "minMessage" => "You must be at least {{ limit }}cm
tall to enter"])>>
<<ORMColumn(ORMColumn::T_INTEGER)>>
protected $height;
<<ORMManyToMany(Phonenumber::class)>>
<<ORMJoinTable("users_phonenumbers")>>
<<ORMJoinColumn("user_id", "id")>>
<<ORMInverseJoinColumn("phonenumber_id", "id", JoinColumn::UNIQUE)>>
private $phonenumbers;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/etes-vous-pret-pour-php8-200910065911/85/Etes-vous-pret-pour-php8-19-320.jpg)










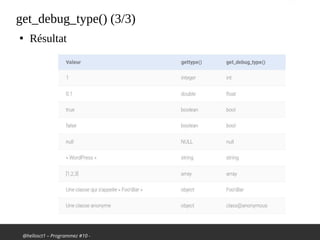
![@hellosct1 – Programmez #10 -
get_debug_type() (2/3)
●
PHP 8
if (!($bar instanceof Foo)) {
throw new TypeError(
'Expected ' . Foo::class .
' got ' . get_debug_type($bar));
}
Avant :
$bar = [1,2,3];
if (!($bar instanceof Foo)) {
throw new TypeError(
'Expected ' . Foo::class .
', got ' . (is_object($bar) ? get_class($bar) : gettype($bar)));
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/etes-vous-pret-pour-php8-200910065911/85/Etes-vous-pret-pour-php8-30-320.jpg)