Diuretics
- 1. Diuretics By Dr. Dinesh Kumar G Pharm. D
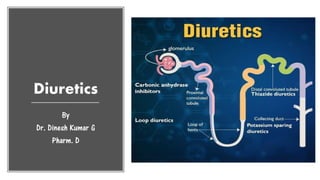
- 3. CLASSIFICATION 1. High efficacy diuretics (Inhibitors of Na+- K+-2Cl¯ cotransport) Furosemide, Bumetanide, Torasemide, azosemide, ethacrynic acid 2. Medium efficacy diuretics (Inhibitors of Na+-Cl¯ symport) I. Benzothiadiazines (thiazides): Chlorothiazide, Hydrochlorothiazide, Benzthiazide, polythiazide, Hydroflumethiazide, Bendroflumethiazide II. Thiazide like (related heterocyclics): Chlorthalidone, Metolazone, Xipamide, Indapamide, Clopamide 3. Weak or adjunctive diuretics I. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors – Acetazolamide, methazolamide, dorzolamide. II. Potassium sparing diuretics a) Aldosterone antagonist: Spironolactone, Eplerenone b) Inhibitors of renal epithelial Na+ channel: Triamterene, Amiloride. III.Osmotic diuretics: Mannitol, Isosorbide, Glycerol
- 4. HIGH CEILING (LOOP) DIURETICS (Inhibitors of Na+-K+-2Cl¯ Cotransport) Furosemide: (Prototype drug) Rapidly acting highly efficacious oral diuretic - maximal natriuretic effect Diuretic response - increase with increasing dose - up to 10 L of urine/day. It is active even in patients with relatively severe renal failure. The major site of action is the thick AscLH where furosemide inhibits Na+- K+-2Cl¯ cotransport. The corticomedullary osmotic gradient is abolished and positive as well as negative free water clearance is blocked. K+ excretion is increased mainly due to high Na+ load reaching DT. However, K+ loss is less than that with thiazides. Duration: 3 – 6 hours Onset of Action IV 2 – 5 min IM 10 – 20 min Oral 20 – 40 min
- 6. • Weak CAse inhibitory action; increases HCO3 ¯ excretion as well • The diuretic action is independent of acid-base balance of the body and mild alkalosis occurs at high doses. • In addition to its prominent tubular action, furosemide causes acute changes in renal and systemic hemodynamics. • After 5 min of i.v. injection, renal blood flow is transiently increased and there is redistribution of blood flow from outer to midcortical zone; g.f.r. generally remains unaltered despite increased renal blood flow.
- 7. Dose Usually 20–80 mg once daily in the morning. In renal insufficiency, up to 200 mg 6 hourly has been given by i.m/i.v route. In pulmonary edema 40–80 mg may be given i.v. LASIX 40 mg tab., 20 mg/2 ml inj. LASIX HIGH DOSE 500 mg tab, 250 mg/25 ml inj; (solution degrades spontaneously on exposure to light), SALINEX 40 mg tab, FRUSENEX 40, 100 mg tab
- 8. Use of high ceiling diuretics 1. Edema 2. Acute pulmonary edema (acute LVF, following MI) 3. Cerebral edema 4. Hypertension 5. Hypercalcaemia of malignancy 6. Along with blood transfusion in severe anaemia, to prevent volume overload. 7. Infused with hypertonic saline, it may be helpful in hyponatraemia.
- 9. THIAZIDE AND RELATED DIURETICS (Inhibitors of Na+-Cl¯ symport) Thiazides Reach distal tubule Bind to and block Na+Cl- cotransport system Increases excretion of Na+ and Cl- Other effects • Also inhibit carbonic anhydrase and bicarbonate loss • Reduces excretion of calcium and uric acid • Increases the excretion of magnesium and potassium Duration: 6 - 48 hours Onset of Action – within 60 mins
- 11. Uses 1. Edema 2. Hypertension 3. Diabetes insipidus 4. Hypercalciuria Drug Daily dose (mg) Duration of action (hr) Hydrochlorothiazide 12.5–100 6–12 Chlorthalidone 50–100 48 Metolazone 5–20 12–24 Indapamide 2.5–5 12–24 Clopamide 10–60 12–18
- 12. THIAZIDE AND LOOP DIURETICS DRUG NAME chlorothiazide, hydrochlorothiazide, indapamide furosemide, bumetanide, ethacrynic acid, torsemide CLASS Thiazide and thiazide-like diuretics Loop diuretics MECHANISM OF ACTION Inhibit sodium-chloride channels in the distal convoluted tubules → prevent the reabsorption of sodium and chloride → salt and water excretion Inhibit Na-K-2Cl transporter in the thick ascending limb of loop of Henle → excretion of sodium, potassium, and chloride → water excretion INDICATIONS Hypertension, Pulmonary edema, Heart failure, Edema caused by renal and hepatic diseases ROA PO, IV PO, IV, IM SIDE EFFECTS •Hypercalcemia, uricemia, cholesterolemia, glycemia •Hypomagnesemia, chloremia, natremia, kalemia •Metabolic alkalosis •Increased LDL •Hypomagnesemia, chloremia, natremia,kalemia •Metabolic alkalosis •Hypotension •Hyperglycemia CONTRA - INDICATIONS AND CAUTIONS •Gout •Diabetes mellitus •Hyperlipidemia •Renal failure with anuria •Existing electrolyte imbalance •Renal failure with anuria •Hepatic encephalopathy •Diabetes mellitus CLIENT EDUCATION Include foods containing potassium in diet; e.g., bananas, potatoes. Blood pressure self-monitoring and routine laboratory tests needed during therapy Report symptoms of hypokalemia; e.g., muscle cramps, heart palpitations, ototoxicity; e.g., ringing in the ears (tinnitus), dizziness, decreased hearing
- 13. CARBONIC ANHYDRASE INHIBITORS Carbonic anhydrase (CAse) is an enzyme which catalyzes the reversible reaction H2O + CO2 ⇌ H2CO3. Carbonic anhydrase thus functions in CO2 and HCO3 ¯ transport and in H+ ion secretion. The enzyme is present in renal tubular cell (especially PT) gastric mucosa, exocrine pancreas, ciliary body of eye, brain and RBC. In these tissues a gross excess of CAse is present, more than 99% inhibition is required to produce effects.
- 14. Acetazolamide A sulfonamide derivative is a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor and enhances the excretion of sodium, potassium and bicarbonate and water. The loss of bicarbonate leads to metabolic acidosis. The enzyme is present in renal tubular cell(especially PT) gastric mucosa, exocrine pancreas, ciliary body of eye, brain and RBC. Acetazolamide Binds to and inhibits enzyme carbonic anhydrase Blocks NaHCO3 - Increased excretion of Na+, K+, HCO3 - and water Dose: 250 mg OD–BD Duration: 8 - 12 hours Onset of Action – within 90 mins
- 15. The extrarenal actions of acetazolamide are: (i) Lowering of intraocular tension due to decreased formation of aqueous humor (aqueous is rich in HCO¯3). (ii) Decreased gastric HCl and pancreatic NaHCO3 secretion: This action requires very high doses—not significant at clinically used doses. (iii) Raised level of CO2 in brain and lowering of pH →sedation and elevation of seizure threshold. (iv) Alteration of CO2 transport in lungs and tissues. These actions are masked by compensatory mechanisms.
- 16. Uses Because of self-limiting action, production of acidosis and hypokalemia, acetazolamide is not used as diuretic. Its current clinical uses are: 1. Glaucoma: as adjuvant to other ocular hypotensive 2. To alkalinize urine: for urinary tract infection or to promote excretion of certain acidic drugs. 3. Epilepsy: as adjuvant in absence seizures when primary drugs are not fully effective. 4. Acute mountain sickness: for symptomatic relief as well as prophylaxis. Benefit occurs probably due to reduced CSF formation as well as lowering of CSF and brain pH. 5. Periodic paralysis.
- 17. Osmotic Diuretics – Mannitol Mannitol Filtered freely by glomerulus and Increases osmolarity of tubular fluid and plasma osmolarity Shifts fluid from ICF to ECF and increases ECF volume and Increases urine formation Water retained in PCT and descending limb of Henle’s loop Increased water diuresis Dose: 1 – 2 g/kg IV infusion
- 20. DIURETICS: OSMOTIC AND CARBONIC ANHYDRASE INHIBITORS DRUG NAME mannitol acetazolamide, dichlorphenamide, methazolamide, brinzolamide, dorzolamide CLASS Osmotic diuretics Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors MECHANISM OF ACTION Freely filtered into the tubules → increases osmolality of the tubular fluid → draws water into the tubules for excretion along with mannitol Inhibit carbonic anhydrase enzyme in the renal tubules → decrease absorption of bicarbonate and sodium → diuresis •Inhibit carbonic anhydrase enzyme in the eyes → decrease production of the aqueous humor → decrease intraocular pressure INDICATIONS •Glaucoma •Increased intracranial pressure •Induce renal excretion of toxic substances (myoglobin from rhabdomyolysis, hemoglobin from hemolysis) •Adjuncts to other diuretics for edematous conditions (e.g., heart failure, pulmonary edema) •Cystinuria •Gout •Open-angle glaucoma ROA IV PO, IV, Opth
- 21. SIDE EFFECTS •Exacerbation of fluid overload conditions •Dehydration •Hypotension •Confusion •Nausea •Vomiting •Metabolic acidosis •Hypokalemia •Hyperchloremia •Neurological side effects, e.g., headache, seizures, mental status changes, paraesthesia •Gastrointestinal side effects, e.g., altered sense of taste, nausea, vomiting and diarrhea •Side effects with IV forms: hepatic necrosis, agranulocytosis, aplastic anemia CONTRA - INDICATIONS AND CAUTIONS •Renal failure with anuria •Fluid overload conditions (e.g., heart failure, pulmonary edema) •Dehydration •Severe renal or hepatic disease (e.g., cirrhosis) •Electrolyte abnormalities (e.g., hyponatremia, hyperkalemia) •Respiratory acidosis •Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease •Sulfa allergy
- 22. ASSESSMENT AND MONITORING Baseline assessment Patent IV, indwelling urinary catheter, ICP monitor •Vital signs, lung sounds, SpO2, weight, BUN, creatinine, electrolytes, serum mOsm, urinalysis, urine out 30–50 mL/hr; neurological status •Check the mannitol solution crystals; warm solution to dissolve; use an in-line filter Monitoring Vital signs, lung sounds, SpO2, electrolytes, BUN, creatinine, I & O •Signs of fluid overload; signs of hypovolemia and hypotension •Notify the health care provider for serum sodium more than 150 mEq/L or serum osmolality more than 320 mOsm •Signs of IV site infiltration •Therapeutic response: decreased ICP, improved level of consciousness, increased urine output •Rebound increased ICP •Patient IV site •Baseline assessment: blood gas analysis, CBC, platelets, glucose, BUN, creatinine, liver function tests •Monitor CBC, platelets, blood gas analysis; glucose for diabetic clients •Therapeutic response: decreased edema, normal acid- base balance CLIENT EDUCATION •Purpose of medication •Report trouble breathing, headache, blurred vision, or pain at the IV site
- 23. POTASSIUM SPARING DIURETICS Spironolactone • It is a steroid, chemically related to the mineralocorticoid aldosterone. • Aldosterone penetrates the late DT and CD cells and acts by combining with an intracellular mineralocorticoid receptor (MR) induces the formation of ‘aldosterone-induced proteins’(AIPs). • The AIPs promote Na+ reabsorption and K+ secretion. • Spironolactone acts from the interstitial side of the tubular cell, combines with MR and inhibits the formation of AIPs in a competitive manner. • It has no effect on Na+ and K+ transport in the absence of aldosterone, while under normal circumstances, it increases Na+ and decreases K+ excretion. Spironolactone Binds aldosterone receptor Inhibits action of aldosterone Increases sodium and water excretion, and decreases potassium excretion
- 25. Use 1. To counteract K+ loss due to thiazide and loop diuretics. 2. Edema: It is more useful in cirrhotic and nephrotic edema in which aldosterone levels are generally high. Spironolactone is frequently added to a thiazide/loop diuretic in the treatment of ascites due to cirrhosis of liver. It breaks the resistance to thiazide diuretics that develops due to secondary hyperaldosteronism and reestablishes the response. 3. Hypertension: Used as adjuvant to thiazide to prevent hypokalaemia, it may slightly add to their antihypertensive action 4. CHF Dose: 25–50 mg BD–QID; max 400 mg/day
- 26. POTASSIUM SPARING DIURETICS Amiloride Amiloride Bind to sodium channels on DCT and CD Increases sodium excretion and retain potassium Dose: 5 – 10 mg OD - BD T1/2 – 20 hours
- 28. POTASSIUM-SPARING DIURETICS DRUG NAME spironolactone, eplerenone amiloride, triamterene CLASS Potassium-sparing diuretics MECHANISM OF ACTION Block aldosterone receptors → decrease the synthesis of epithelial sodium channels (ENaC) and hydrogen pumps → increase sodium excretion, and decrease potassium and hydrogen excretion Block ENaC → increase sodium excretion, while preserving potassium INDICATIONS •Hypertension •Pulmonary edema •Heart failure •Edema caused by renal and hepatic diseases •Hyperaldosteronism (spironolactone) ROA PO SIDE EFFECTS •Hyperkalemia •Metabolic acidosis •Gynecomastia •Impotence •Hyperkalemia •Metabolic acidosis •Kidney stones CONTRAINDICATIO NS AND CAUTIONS •Hyperkalemia •Renal failure with anuria •Severe liver diseases CLIENT EDUCATION •Avoid high-potassium foods and salt substitutes Report Nausea, vomiting, muscle twitching or cramps, trouble breathing, heart palpitations •Endocrine problems; e.g., menstrual irregularities, gynecomastia, impotence
- 29. Thank You