Pedo ecc
- 1. EARLY CHILDHOOD CARIES MAKAL MADHAV MP FINAL YEAR PART II 100020257
- 2. CONTENTS • Definition • Classification • Stages of development of ECC • Etiology • Diagnosis • Prevention • Management • conclusion
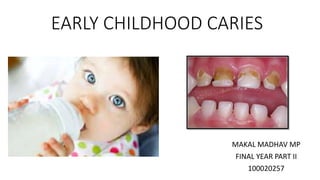
- 3. Defintion AMERICAN ACADEMY OF PEDIATRIC DENTISTRY (AAPD) : The presence of one or more decayed ( non cavitated , cavitated ) , missing ( due to caries ) or filled tooth surface in any primary tooth in a child 71 months of age or younger .The academy also specifies that , in children younger than 3 years , any sign of smooth surface caries is indicative of severe ECC DAVIS ( 1998 ) : Complex disease involving maxillary primary incisors within a month after eruption and spreading rapidly to other primary teeth is called childhood caries
- 4. • TERMINOLOGY USED FOR ECC 1) Nursing bottle caries 2) Baby bottle tooth decay 3) Nursing bottle syndrome 4) Milk bottle syndrome 5) Tooth clearing neglect -Moss ( 1996) 6) Infant and Early childhood dental decay - Horowitz 7) MDSMD – Maternally Derived Streptococcus Mutans Disease
- 5. CLASSIFICATION OF ECC TYPE I Mild to moderate isolated caries lesions involving molars and incisors number of carious teeth increase as cariogenic semi solid food and lack of oral hygiene seen in 2-5 years old
- 6. Type II : moderate to severe labiolingual carious lesion affecting maxillary incisors mandibular incisors are not affected use of feeding bottle or at will breast feeding or a combination of both with or without poor oral hygiene seen soon after eruption of teeth
- 7. Type III severe Carious lesion involve almost all the teeth including mandibular incisors Usually seen in 3-5 years of age cause is a combination of factors and a poor oral hygiene Rampant in nature and involves immune tooth surface
- 8. DEVELOPMENTAL STAGES OF ECC Stage 1 : Initial reversible stage 10 – 20 months Maxillary anterior teeth opaque white demineralization In cervical or interproximal region no pain
- 9. Stage II : Damaged carious stage 16-24 months lesion in maxillary anterior teeth ,may spread tp dentin and show yellowish brown discoloration pain on having cold food items
- 10. Stage III : deep lesions 24-36 months depending on time of eruption , carogenicity of sweetner and frequecy of its use ,this stage can be reached in 10-14 months also molars are also affected frequent complaint of pain due to pulpal involvement in maxillary incisors
- 11. Stage 1V : Traumatic stage 36-48 months teeth become so weakened by caries that relatively small force can fracture patient may report a history of trauma molars are anow associated with pulpal problems maxillary incisors becomes non vital
- 12. Initially, a demineralization dull, white area is seen along the gum line on labial aspect of maxillary incisors. These white lesions become cavities which involve the neck of the tooth in a ring like fashion Finally, the whole crown of the incisors is destroyed leaving behind brown-black root stumps.
- 13. ETIOLOGY • Bovine milk,milk formulas, and human breast milk have all seen implicated nursing caries because of their lactose content • Basic mechanism of demineralization is same and caries tetralogy is key in whole process(microbes,substrates,host,time) • Pathogenic microorganism- streptococcus mutans
- 14. Etiological agents in nursing bottle caries Pathogenic microorganisms Substrate (fermentable carbohydrates) Host Time Other predisposing factors
- 15. • Steptococcus mutans- main microbe that colonizes teeth after it erupts into oral cavity. • It is transmitted to infant’s mouth through mother. • It is more virulent because:- • It colonizes the teeth • It produces large amount of acid • It produces large amount of extracellular polysaccharides that favor plaque formation.
- 16. SUBSTRATE (fermentable carbohydrate) • Carbohydrates are converted into dextrans by microorganisms. • In infants & toddlers, the main sources of fermentable carbohydrates are: i. Bovine milk or infant formulas ii. Human milk (breast-feeding at will) iii. Fruit juices & other sweet liquids iv. Sweet syrups like vitamin preparations v. Pacifiers dipped in honey or sugar solution vi. Chocolates or other sweets
- 17. HOST • Teeth act as host for microorganisms • Hypomineralisation or hypoplasia of teeth increases the susceptibility of child to caries • Thin enamel in primary teeth is one of the reasons for early spread of lesions • Developmental grooves also may act as plaque retentive areas
- 18. TIME • More the time child sleeps with bottle in the mouth the higher is the risk of caries because the salivary flow and the swallowing reflex decrease, thus providing more time for accumulation of carbohydrates in the mouth which are acted upon by microbes to produce acid leading to caries.
- 19. CLINICAL FEATURES Mandibular molars: at later stage Maxillary canines & 2nd molars: facial, lingual, proximal surfaces Maxillary 1st molars: facial, lingual, occlusal, proximal surfaces Maxillary lateral incisors: facial, lingual, mesial, distal surfaces Maxillary central incisors: facial, lingual, mesial, distal surfaces
- 20. • Mandibular anterior teeth are usually spared because of: I. Protection by tongue II. Cleansing action of saliva due to presence of the orifice of the duct of sublingual glands very close to lower incisors.
- 21. • DIAGNOSIS OF ECC Health Policy Bureau , Ministry of Health and Welfare C0 : Caries with only white lesions without visual decay C1 : Caries in enamel C2 : Caries in dentin C3 : Caries with perforation ito pulp C4 : Caries with existence to root
- 22. • CARIES ACTIVITY TEST Cariostat Blue ( ph 7.0 ) = 0 Green yellow ( 4.4)= 2 Green ( ph 5.4) – 1 Yellow ( 4.0) = 3
- 23. PREVENTION OF ECC 1) Community based education 2 ) examination and preventive care in dental clinic 3) development of appropriate dietary and self care habits at home .
- 24. AAPD RECOMENDATIONS FOR PREVENTION OF ECC • Infants shouldnot be put to sleep with a bottle . • Nocturnal breast feeding should be avoided a Parents should be encouraged to have infants drink from a cup • • Oral hygiene measures should be implemented by the time of eruption of the first primary tooth . • An oral health consumption visit is recommended ( educate the parent and for pravention
- 25. RAPIDD SCALE • The readiness assessment of parents concerning infant dental decay scale was developed to assess a parents stage of change - precontemplative , contemlative or action with regard to his / her childs dental health .
- 26. PROFESSIONAL AND HOME BASED PREVENTIVE APPROACHES • No signs of ECC or low ECC risk status a) Fluoridated dentifrices b) Review of dietary and oral hygiene • Signs of ECC OR high ECC risk status a) Fluoride varnish b) Sealants c) Chlorhexidine varnish d) Xylitol pacifiers e) Fluoridated supplements and dentifrices f) Dietary counseling
- 27. MANAGEMENT • This can be divided into : 1) Discontinuation of the habit 2) Restorative procedures 3) Education
- 28. • Discontinuation of the habit < identify the cause < gradual withdrawal rather than abrupt cessation of the habit < feeding with cup or spoon is encouraged < serial dilution of the contents of the bottle with water • < Clearance of the milk can be aided by intake of water after feed. • < Infants must be weaned at 12 to 14 months of age .
- 29. 2) Dietary modifications • Elimination or gradual reduction of sugar must be done • Depending on the child age and chewing capacity natural foods like fruits should be given • Oral hygiene measures should be implemented
- 30. RESTORATIVE PROCEDURES involves thorough excavations followed by placement of sedative dressings > patient is then given necessary information regarding oral hygiene and diet. > on subsequent visit further treatment are carried out. small restorations : composite resins , amalgam and GIC Pulp involvement : indirect or direct pulp capping , pulpotomy , pulpectomy as indicated.
- 31. DENTAL HEALTH EDUCATION • play an important role both in prevention and treatment of nursing caries. Expectant women and mothers should be taught how to take care of their baby’ s teeth regular tooth cleaning twice a day after feeding will have significant impact
- 32. TREATMENT : 1ST VISIT All lesions should be excavated and restored Indirect pulp capping or pulp therapy procedures can be evaluated by further investigation If the abscess is present it can be treated by drainage X-Rays are advised to assess the condition of succedaneous teeth collection of saliva for determining the salivary flow & viscosity Also, application of fluoride topically
- 33. PARENT COUNCELLING Parent should be questioned about the child’s feeding habits, nocturnal bottles, demand for breast-feeding, pacifiers. Parents should be asked to try weaning the child from using the bottle as pacifier while in bed. In case of emotional dependence on the bottle, suggest use of plain or fluoridated water. The parents should be instructed to clean the child’s teeth after every feed. Parents are advised to maintain a diet record of the child for 1 week that includes the time, amount of food given to the child, the type of the food & the number of sugar exposures.
- 34. 2nd VISIT Should be scheduled 1 week after 1st week. Analysis of diet chart & explanation of disease process of child’s teeth Isolate the sugar factors from diet chart & control sugar exposure Reassess the restoration and redo if needed Caries activity tests can be started & repeated at monthly interval to monitor the success of treatment
- 35. 3rd & SUBSEQUENT VISITS • Restoring all grossly decayed teeth • Endodontic treatment • In case of unrestorable teeth, extraction followed by space maintainer • Crowns given for grossly decayed & endodontically treated teeth • Review & recall after every 3 months
- 36. CONCLUSION • ECC is a specific term used to describe a unique pattern of dental decay in infants and toddlers and preschool children • Proprer reassurance and education is necessary to prevent ECC
- 37. REFERENCE • Dentistry of child and adolescent –Mc DONALD • Text book of pediatric dentistry –Nikhil Marwah • Principles and practice of pedodontics – Arathi Rao • Text book of pedodontics –shobha Tandon