Lec52
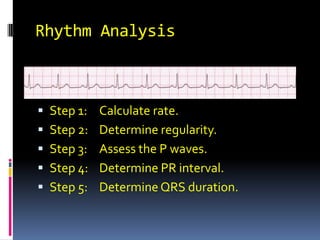
- 1. Rhythm Analysis Step 1: Calculate rate. Step 2: Determine regularity. Step 3: Assess the P waves. Step 4: Determine PR interval. Step 5: Determine QRS duration.
- 2. Step 1: Calculate Rate Option 1 Count the # of R waves in a 6 second rhythm strip, then multiply by 10. Interpretation? 3 sec 3 sec 9 x 10 = 90 bpm
- 3. Step 1: Calculate Rate Option 2 Find a R wave that lands on a bold line. Count the # of large boxes to the next R wave. If the second R wave is 1 large box away the rate is 300, 2 boxes - 150, 3 boxes - 100, 4 boxes - 75, etc. (cont) R wave
- 4. Step 1: Calculate Rate Option 2 Interpretation? 300 150 100 75 60 50 Approx. 1 box less than 100 = 95 bpm
- 6. What is the heart rate?
- 7. Step 2 : Determine Regularity Regular: If the difference between the longest R-R interval in the ECG and the shortest R-R interval is less than 0.12 second Irregular: If the difference between the longest R-R interval in the ECG and the shortest R-R interval is greater than 0.12 second
- 8. Step 2: Determine regularity Look at the R-R distances (using a caliper or markings on a pen or paper). Interpretation? R R Regular
- 9. Step 3: Assess the P waves Are there P waves? Do the P waves all look alike? Do the P waves occur at a regular rate? Is there one P wave before each QRS? Interpretation? Normal P waves with 1 P wave for every QRS
- 10. Step 4: Determine PR interval Normal: 0.12 - 0.20 seconds. (3 - 5 boxes) Interpretation? 0.12 seconds
- 11. Step 5: QRS duration Normal: 0.04 - 0.12 seconds. (1 - 3 boxes) Interpretation? 0.08 seconds
- 12. Rhythm Summary Rate 90-95 bpm Regularity regular P waves normal PR interval 0.12 s QRS duration 0.08 s Interpretation? Normal Sinus Rhythm
- 13. Normal Sinus Rhythm (NSR) The electrical impulse is formed in the SA node and conducted normally. This is the normal rhythm of the heart; other rhythms that do not conduct via the typical pathway are called arrhythmias.
- 14. NSR Parameters Rate 60 - 100 bpm Regularity regular P waves normal PR interval 0.12 - 0.20 s QRS duration 0.04 - 0.12 s
- 15. Cardiac Arrhythmias and Their Electrocardiographic Interpretation Abnormal rhythmicity of the pacemaker Shift of the pacemaker from the sinus node to another place in the heart Blocks at different points in the spread of the impulse through the heart Abnormal pathways of impulse transmission through the heart Spontaneous generation of spurious impulses in almost any part of the heart
- 16. Tachycardia: The term "tachycardia" means fast heart rate, usually defined in an adult person as faster than 100 beats per minute This electrocardiogram is normal except that the heart rate The general causes of tachycardia include increased body temperature, stimulation of the heart by the sympathetic nerves, or toxic conditions of the heart Abnormal Sinus Rhythms
- 19. Sinus Tachycardia Deviation from NSR - Rate > 100 bpm
- 20. Sinus Tachycardia SA node is depolarizing faster than normal, impulse is conducted normally.
- 21. Bradycardia The term "Bradycardia" means a slow heart rate, usually defined as fewer than 60 beats per minute The cause of Bradycardia is Vagal Stimulation
- 24. Sinus Bradycardia Deviation from NSR - Rate < 60 bpm
- 25. Sinus Bradycardia SA node is depolarizing slower than normal, impulse is conducted normally (i.e. normal PR and QRS interval).
- 26. Atrioventricular Block Delay or blocks conduction from the atria to the ventricles. Causes are ischemia, extreme stimulation of the heart by vagus nerves, inflammation of the AV node or A-V bundle
- 27. 1st Degree AV Block Prolonged conduction delay in the AV node or Bundle of His.
- 30. 1st Degree AV Block Deviation from NSR PR Interval > 0.20 s
- 31. 2nd Degree Block When conduction through the A-V bundle is slowed enough to increase the P-R interval to 0.45 second. There will be P wave but no QRS-T wave There is drop beat of the ventricles
- 35. 2nd Degree AV Block Deviation from NSR PR interval progressively lengthens, then the impulse is completely blocked (P wave not followed by QRS).
- 36. 3rd Degree AV Block Deviation from NSR The P waves are completely blocked in the AV junction; QRS complexes originate independently from below the junction.
- 37. 3rd Degree AV Block There is complete block of conduction in the AV junction, so the atria and ventricles form impulses independently of each other. Without impulses from the atria, the ventricles own intrinsic pacemaker kicks in at around 30 - 45 beats/minute.
- 40. Premature Contractions A premature contraction is a contraction of the heart before the time that normal contraction would have been expected. This condition is also called extrasystole, premature beat, or ectopic beat The causes are local areas of ischemia, toxic irritation of A-V node, purkinje system caused by drugs or caffeine
- 41. Premature Atrial Contractions Deviation from NSR These ectopic beats originate in the atria (but not in the SA node), therefore the contour of the P wave, the PR interval, and the timing are different than a normally generated pulse from the SA node.
- 44. Premature Ventricular Contraction Deviation from NSR Ectopic beats originate in the ventricles resulting in wide and bizarre QRS complexes. The QRS complex is usually prolonged. The reason is that the impulse is conducted mainly through slowly conducting muscle of the ventricles
- 47. Atrial Fibrillation Deviation from NSR No organized atrial depolarization, so no normal P waves The cause of atrial fibrillation is atrial enlargement resulting from heart valve lesions that prevent the atria from emptying adequately into the ventricles
- 48. Atrial Fibrillation Recent theories suggest that it is due to multiple re-entrant wavelets conducted between the R & L atria. Either way, impulses are formed in a totally unpredictable fashion. The AV node allows some of the impulses to pass through at variable intervals (so rhythm is irregularly irregular).
- 51. Ventricular Fibrillation The ventricular cells are excitable and depolarizing randomly. Rapid drop in cardiac output and death occurs if not quickly reversed
- 52. Ventricular Fibrillation Deviation from NSR Completely abnormal.
