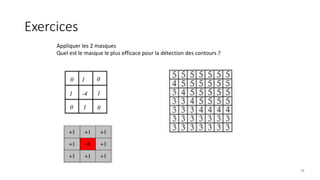
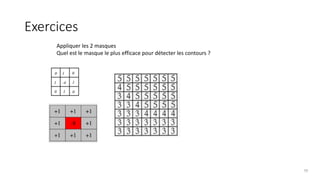
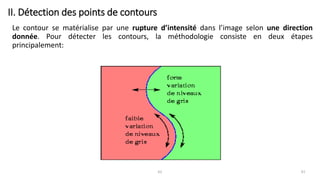
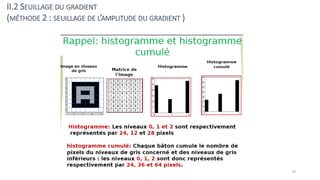
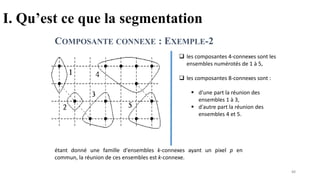
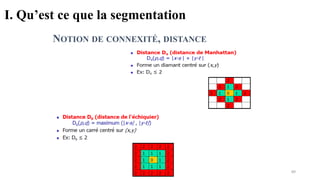
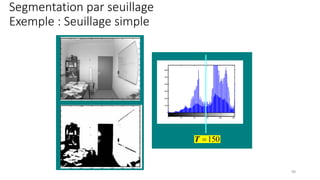
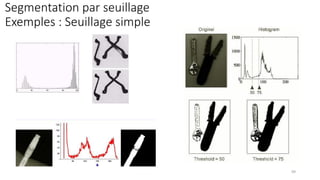
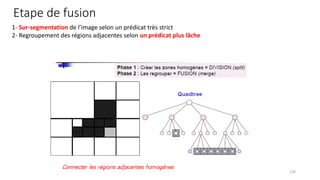
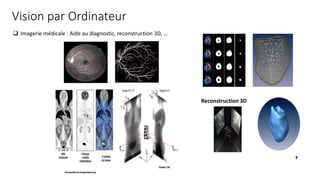
Computer vision is transforming industries by enabling computers to interpret and analyze visual data, bridging the gap between human perception and machine intelligence. This course provides a comprehensive introduction to computer vision, covering fundamental concepts, core techniques, and advanced applications. Designed for students, engineers, and professionals, it offers a balance between theory and practical implementation to help learners build real-world computer vision solutions.
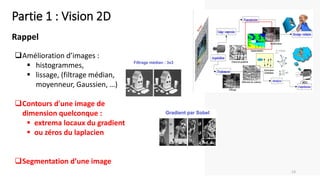
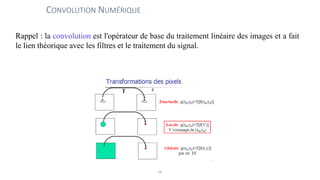
The course begins with an overview of image processing, where students will learn about digital images, color spaces, and image transformations. Fundamental operations such as filtering, edge detection, thresholding, and morphological transformations will be covered, along with techniques for image enhancement and noise reduction. These concepts form the basis for more advanced topics in object detection, image segmentation, and feature extraction.
A key component of the course is feature-based image analysis, which includes detecting and describing key points using algorithms such as SIFT, SURF, ORB, and FAST. Learners will explore how to match features across images and apply these techniques in applications like image stitching and panorama creation. Optical flow and motion tracking will be introduced to analyze moving objects in videos, providing a foundation for video-based applications.
Deep learning has revolutionized computer vision, and this course integrates neural networks and deep learning frameworks to solve complex vision tasks. Students will work with convolutional neural networks (CNNs) to classify images, detect objects, and segment images. The course covers the architecture and inner workings of CNNs, including convolutional layers, pooling layers, activation functions, and backpropagation. Learners will implement models using popular frameworks such as TensorFlow and PyTorch.
Beyond basic CNNs, the course explores state-of-the-art architectures such as ResNet, MobileNet, and Vision Transformers. Transfer learning and data augmentation techniques will be introduced to improve model performance with limited datasets. Object detection methods like YOLO and Faster R-CNN will be covered in detail, allowing students to build applications capable of detecting multiple objects in real-time. Image segmentation techniques such as U-Net and Mask R-CNN will be explored to perform pixel-level classification for medical imaging, autonomous driving, and other domains.
The course also delves into generative models, including Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) and Variational Autoencoders (VAEs), to create and manipulate images. Applications such as style transfer, super-resolution, and deepfake generation will be discussed. In addition, students will learn about facial recognition, pose estimation, and emotion detection, which are widely used in security, entertainment, and human-computer interaction.































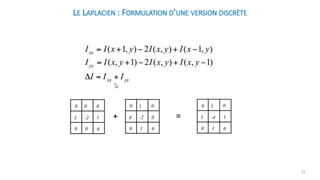
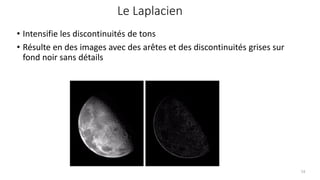
![Le Laplacien : version discrète
• Dérivé partielle seconde de f(x,y) dans la
direction de x
• Dérivé partielle seconde de f(x,y) dans la
direction de y
2
2 1 1 2
f
x
f x y f x y f x y
= + + − −
( , ) ( , ) ( , )
2
2 1 1 2
f
y
f x y f x y f x y
= + + − −
( , ) ( , ) ( , )
= + + −
+ + + − −
2
1 1
1 1 4
f f x y f x y
f x y f x y f x y
[ ( , ) ( , )
( , ) ( , )] ( , )
51](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vision-par-ordinateur-partiecontourssegmenttaion2002-250221170612-169d5def/85/Vision-par-Ordinateur-PartieContourssegmenttaion2002-pdf-51-320.jpg)