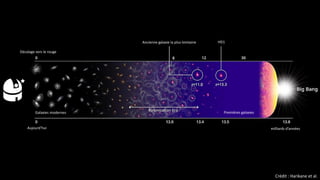
Le document présente des informations sur la découverte des galaxies les plus éloignées, y compris la galaxie HD1 à 33 milliards d'années-lumière. Il met en avant les contributions de divers télescopes, notamment le James Webb Space Telescope, et évoque des illustrations et des données astronomiques. Plusieurs crédits sont attribués aux images et aux recherches mentionnées dans le texte.