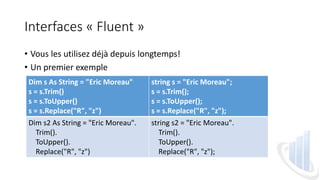
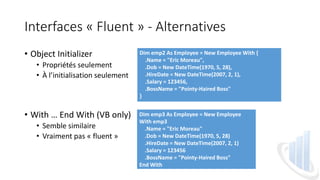
Le document présente l'utilisation des interfaces 'fluent' dans les classes .NET, définies comme une API orientée objet visant à rendre le code plus lisible grâce à la méthode de chaînage. Il donne des exemples pratiques et une méthode étape par étape pour intégrer des interfaces fluent dans des classes existantes, notamment à travers l'implémentation d'une interface et l'utilisation de méthodes d'initialisation. L'article souligne que ces interfaces offrent une meilleure expérience utilisateur et s'intègrent bien avec de nouveaux API comme LINQ.