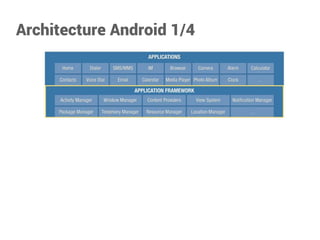
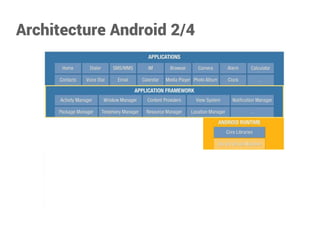
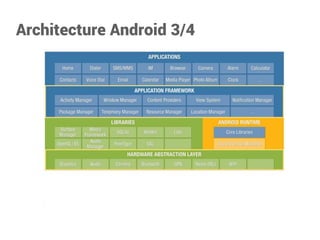
Yoann Gotthilf est un développeur Android, web, et consultant en sécurité avec plus de 13 ans d'expérience. Le document présente une vue d'ensemble d'Android en tant que plateforme mobile, son architecture, ses ressources et les composants essentiels pour le développement d'applications. Il traite également des mécanismes de gestion du cycle de vie des applications et des interactions entre les différents composants.


















![Ressources L’organisation
Chaque type à son propre répertoire
Nom des fichiers : [a-z0-9_]+.<extention>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductionandroid-140928172617-phpapp01/85/Introduction-a-Android-22-320.jpg)










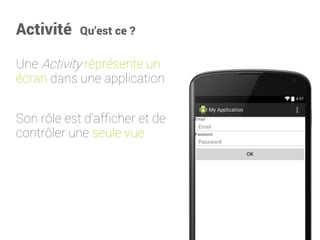


![<LinearLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="vertical">
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textAppearance="?android:attr/textAppearanceMedium"
android:text="@string/connection"
android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal" />
<EditText
android:inputType="textEmailAddress"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:hint="@string/email"
android:id="@+id/email" />
<EditText
android:inputType="textPassword"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:hint="@string/password"
android:id="@+id/password" />
<Button
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@android:string/ok"
android:id="@+id/submit"/>
</LinearLayout>
public class MyActivity extends ActionBarActivity {
private EditText mEmailText ;
private EditText mPasswordText ;
private Button mSubmitButton ;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_my);
mEmailText = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.email);
mPasswordText = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.password);
mSubmitButton = (Button) findViewById(R.id.submit);
}
[...]
}
Activité Récupérer les composants graphiques](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductionandroid-140928172617-phpapp01/85/Introduction-a-Android-37-320.jpg)





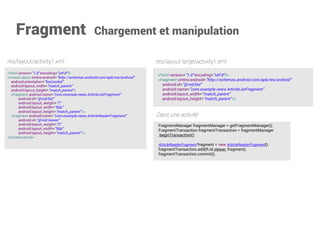



![AdapterView exemple ListView
publicclassList1 extendsListActivity {
@Override
publicvoidonCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.list_1);
ListAdapter adapter=newArrayAdapter<String>(this,
android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1, mStrings);
setListAdapter(adapter);
}
privateString[] mStrings= {
"Abbaye de Belloc", "Abbaye du Mont des Cats", "Abertam", "Abondance", "Ackawi"
};
<TextViewxmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:id="@android:id/text1"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textAppearance="?android:attr/textAppearanceListItemSmall"
android:gravity="center_vertical"
android:paddingStart="?android:attr/listPreferredItemPaddingStart"
android:paddingEnd="?android:attr/listPreferredItemPaddingEnd"
android:minHeight="?android:attr/listPreferredItemHeightSmall"
/>
<LinearLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical">
<TextView
style="?android:attr/textAppearanceLarge"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/cheeses"/>
<ListView
android:id="@android:id/list"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"/>
</LinearLayout>
res/layout/simple_list_item1.xml dans le sdk
res/layout/list_1.xml
List1.java](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductionandroid-140928172617-phpapp01/85/Introduction-a-Android-48-320.jpg)


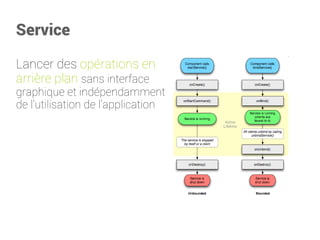





![BroadcastReceiver
<receiver
android:name=".MySMSReceiver">
<intent-filterandroid:priority="100">
<actionandroid:name="android.provider.Telephony.SMS_RECEIVED"/>
</intent-filter>
</receiver>
publicclassMySMSReceiver extendsBroadcastReceiver {
privatefinalString ACTION_RECEIVE_SMS= "android.provider.Telephony.SMS_RECEIVED";
@Override
publicvoidonReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
if(intent.getAction().equals(ACTION_RECEIVE_SMS)) {
Bundle bundle = intent.getExtras();
if(bundle != null) {
Object[] pdus = (Object[]) bundle.get("pdus");
finalSmsMessage[] messages = newSmsMessage[pdus.length];
for(inti = 0; i < pdus.length; i++) {
messages[i] = SmsMessage.createFromPdu((byte[]) pdus[i]);
}
if(messages.length> -1) {
finalString messageBody = messages[0].getMessageBody();
finalString phoneNumber = messages[0]
.getDisplayOriginatingAddress();
Toast.makeText(context, "Expediteur : "+ phoneNumber,
Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
Toast.makeText(context, "Message : "+ messageBody,
Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}
}
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductionandroid-140928172617-phpapp01/85/Introduction-a-Android-57-320.jpg)

