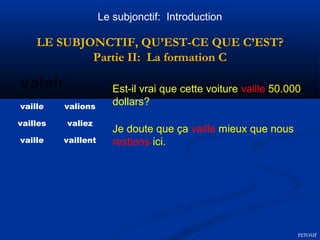
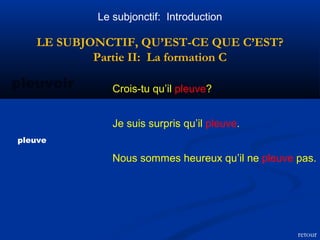
Le document traite du subjonctif en français, expliquant sa définition, son emploi dans les clauses subordonnées et sa formation. Il souligne que le subjonctif est utilisé pour exprimer des sentiments, des doutes, des nécessités, et qu'il dépend de l'attitude du verbe dans la clause principale. De plus, le document présente les règles de formation du subjonctif pour les verbes réguliers et les exceptions pour certains verbes irréguliers.