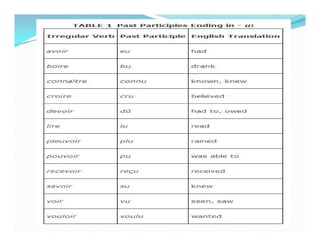
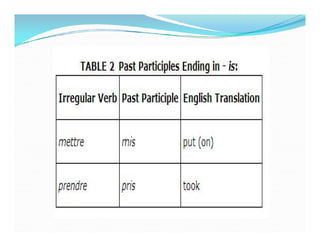
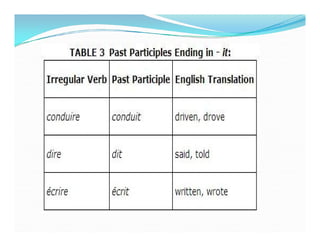
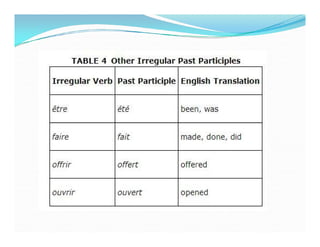
Le futur antérieur est utilisé pour décrire une action future qui aura été réalisée à un moment donné. Il se forme avec le futur simple de 'avoir' ou 'être' suivi du participe passé du verbe principal, en accordant ce dernier selon le type de verbe. Des exemples de conjugaison et d'utilisation en phrases négatives sont également fournis.