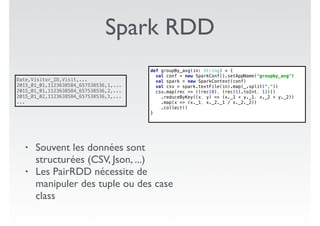
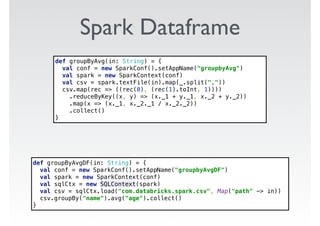
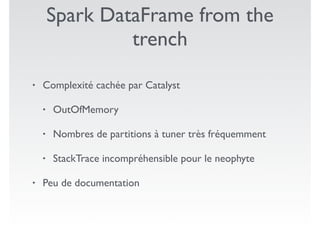
Ce document présente des exemples de code utilisant Apache Spark pour effectuer des opérations de traitement de données, telles que le comptage de mots et le calcul de moyennes à partir de fichiers CSV. Il met en évidence les avantages de Spark, y compris la simplicité d'utilisation par rapport à des bibliothèques comme Pandas, tout en soulignant des défis tels que des erreurs de mémoire et la nécessité de régler le nombre de partitions. Enfin, il aborde des fonctionnalités supplémentaires et des références pertinentes sur Spark.