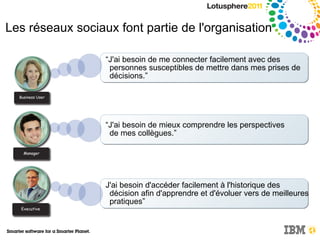
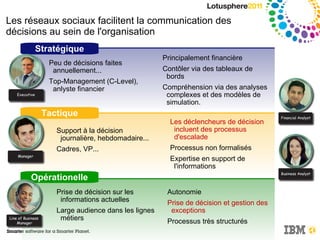
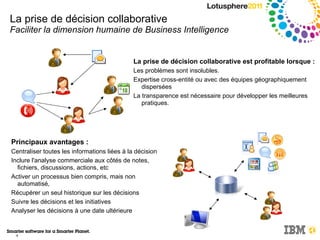
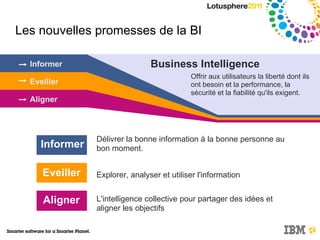
Le document discute de l'intégration de la collaboration dans les processus décisionnels en utilisant IBM Cognos, soulignant l'importance de la business intelligence et des réseaux sociaux pour améliorer la prise de décision. Il met en avant comment la collaboration facilite l'échange d'informations et nécessite une culture organisationnelle adaptée pour optimiser les résultats. Enfin, il propose des exemples pratiques illustrant les bénéfices de décisions collaboratives dans divers secteurs d'activité.