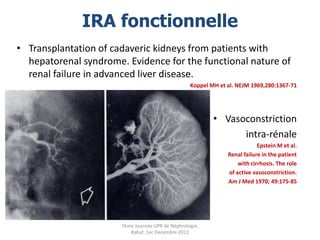
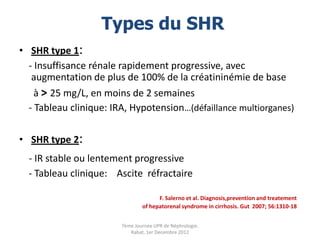
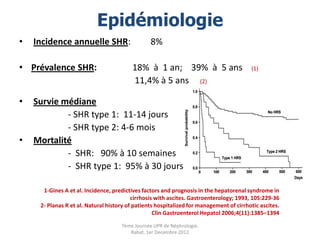
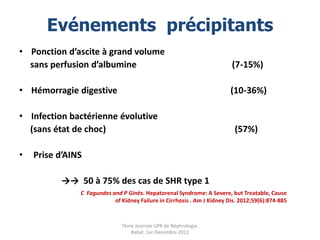
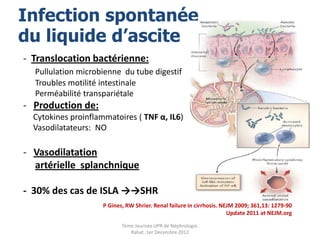
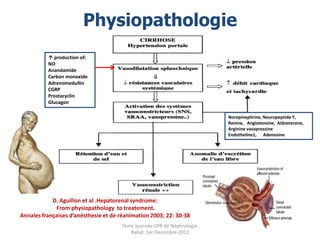
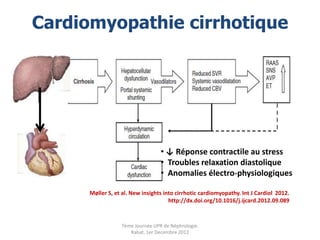
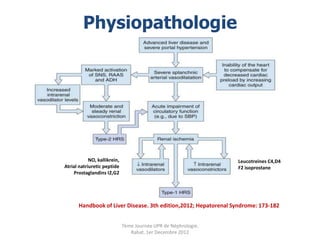
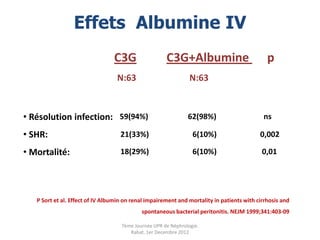
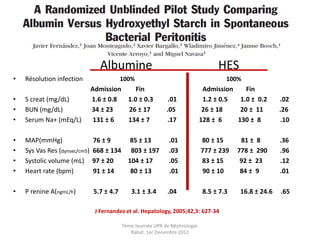
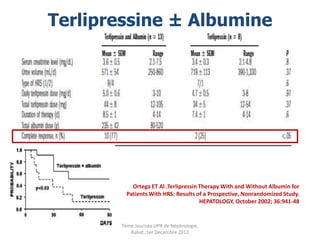
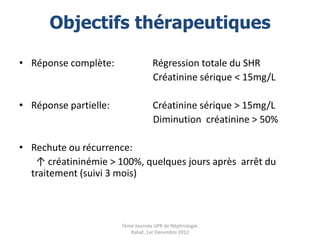
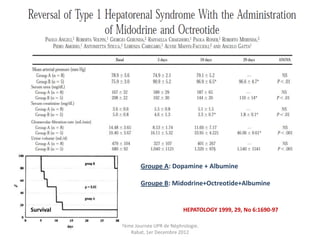
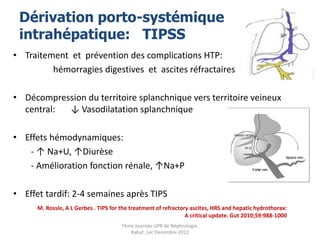
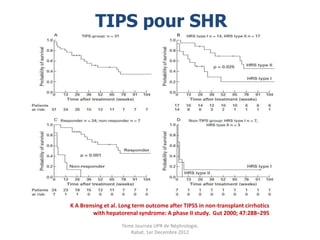
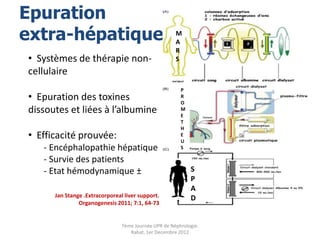
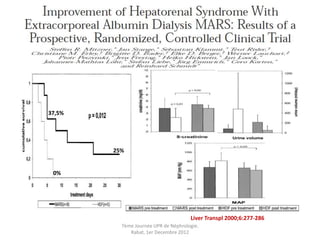
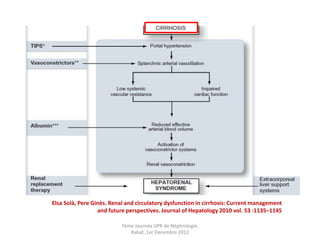
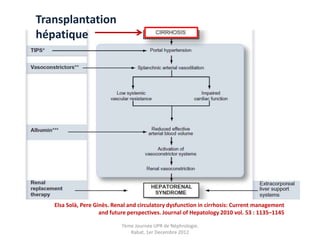
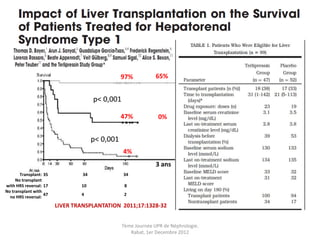
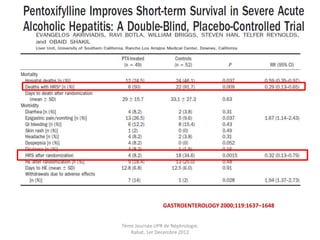
Le document présente le syndrome hépatorénal (SHR), ses définitions, types, critères de diagnostic, épidémiologie et événements précipitants. Il met aussi l'accent sur la physiopathologie, les traitements médicaux comme les analogues de la vasopressine et la thérapie à base d'albumine, ainsi que sur la technique de dérivation porto-systémique intrahépatique (TIPS) comme option de traitement. Les résultats et les données cliniques sur la survie et la réponse au traitement sont discutés en détail.

![SHR: Définition
- Hépatopathie - Insuffisance rénale
avec HTP + ascite fonctionnelle
Cirrhoses Sans cause identifiable
Hépatite alcoolique aigue Oligurie
Hépatite fulminante [Na+] U bas
CHC protéinurie nulle
Hyponatrémie
V.Arroyo; P Gines et al. Definition and diagnosis criteria of refractory ascites and
Hepatorenal Syndrome in cirrhosis. Hepatology 1996; 23,1:164-76
7ème Journée UPR de Néphrologie.
Rabat, 1er Decembre 2012](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lesyndromehepatorenalfinal-121202082748-phpapp02/85/Le-syndrome-hepatorenal-3-320.jpg)